New Digital Map Reveals Nearly 300,000 km of Roman Roads Across the Empire!
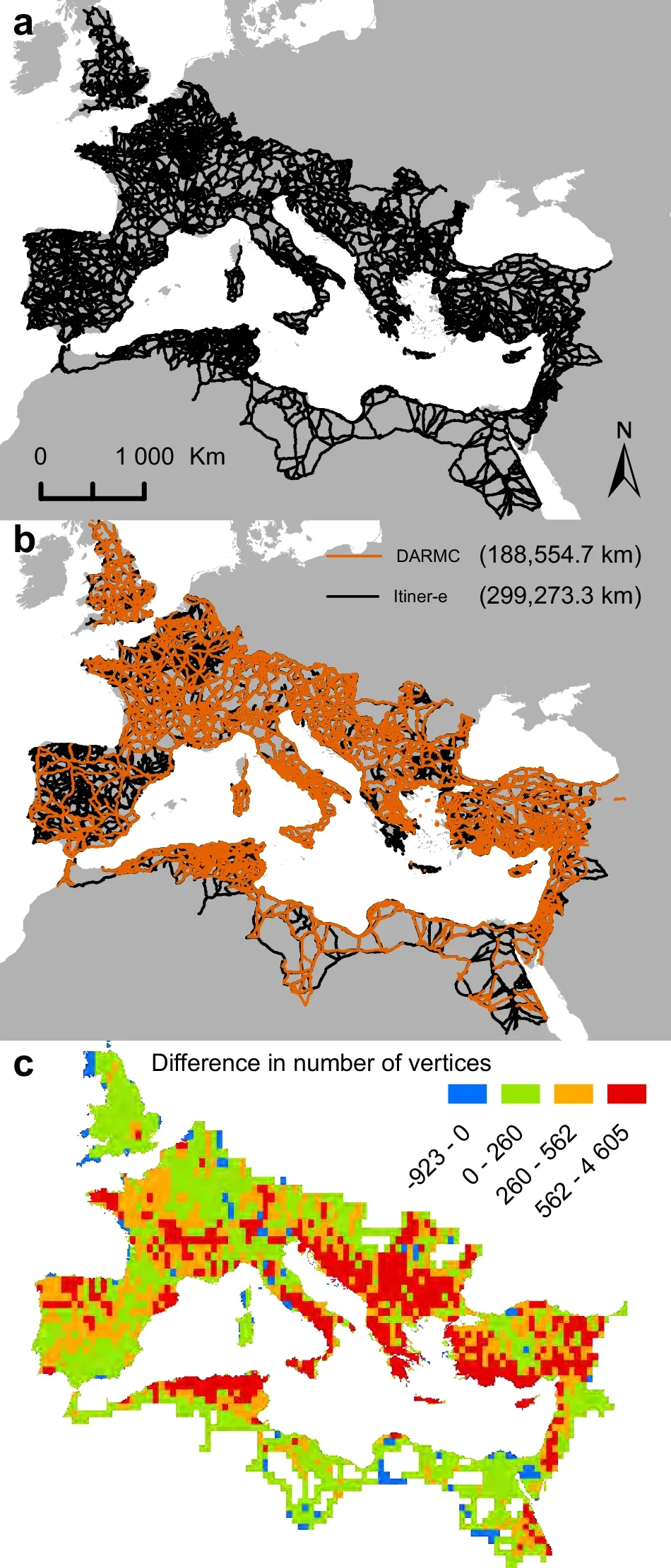
A groundbreaking digital map of Roman roads, named Itiner-e, is offering the most detailed view yet of the Empire’s vast transportation network as it existed around 150 CE. Published in Scientific Data, the dataset nearly doubles the previously known extent of Roman roads, now revealing a total length of 299,171 kilometres across almost four million square kilometres, up from the earlier estimate of 188,555 kilometres.
At its peak in the second century CE, the Roman Empire stretched from Britain to Egypt and Syria, home to over 55 million people. Its intricate road network was essential for administration, trade, military logistics, and cultural exchange. Despite centuries of study, the full extent of this network had never been fully mapped, and earlier digital reconstructions lacked high resolution.
Itiner-e was developed by Tom Brughmans, Pau de Soto, Adam Pažout, and their team, who combined archaeological and historical evidence with modern and historical topographic maps, satellite imagery, and remote sensing techniques.
The researchers divided the roads into 14,769 segments. Of these, 103,478 kilometres (34.6%) are classified as main roads, while 195,693 kilometres (65.4%) are secondary routes. Interestingly, only 2.7% of road locations are known with certainty; nearly 90% are estimated with lower precision, and around 7.4% are hypothesised based on historical and geographical inference.
The dataset also improves coverage in previously underrepresented regions, including the Iberian Peninsula, Greece, and North Africa. It adapts routes to natural geography, such as following winding paths through mountainous terrain instead of drawing straight lines, offering a more accurate picture of how the roads would have actually traversed the landscape.
Researchers describe Itiner-e as a transformative resource for understanding the Roman Empire’s mobility. It will enable scholars to investigate how roads influenced connectivity, trade, migration, administration, and even the spread of diseases.
While this dataset represents the most comprehensive open-source mapping of Roman roads to date, it does not yet track changes over time. However, the project not only consolidates existing knowledge but also highlights gaps in our understanding, paving the way for future research on the evolution of the Empire’s infrastructure and its impact on the ancient world.